Updating deploy script for using UV & CI
November, 09, 2025I've modified the deployment script so it will use UV now for the environment management. First, UV should be installed on the host server.
I've modified the deploy script like this:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -Eeuo pipefail
# Flags
run_tests=false
run_collectstatic=false
python_version=""
env_path=""
usage() {
cat <<EOF
Usage: $0 [-t] [-c] [-p <python_version>] [-e <env_path>]
-t Run Django tests
-c Run "collectstatic"
-p <python_version> Use a specific Python (e.g. 3.12, 3.13)
-e <env_path> Use a specific virtualenv directory (default: .venv)
(uv will honor VIRTUAL_ENV if set)
-h Show this help
Examples:
$0 -t
$0 -c -p 3.13
$0 -t -c -e venv -p 3.12
EOF
}
while getopts ":tcp:e:h" opt; do
case "$opt" in
t) run_tests=true ;;
c) run_collectstatic=true ;;
p) python_version="$OPTARG" ;;
e) env_path="$OPTARG" ;;
h) usage; exit 0 ;;
\?) echo "Unknown option: -$OPTARG" >&2; usage; exit 1 ;;
:) echo "Option -$OPTARG requires an argument." >&2; usage; exit 1 ;;
esac
done
export PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$HOME/.cargo/bin:$PATH"
UV_BIN="${UV_BIN:-$(command -v uv || true)}"
if [[ -z "$UV_BIN" ]]; then
echo "uv not found on PATH: $PATH" >&2
exit 127
fi
# Make UV use a specific env directory if requested
if [[ -n "$env_path" ]]; then
# uv respects VIRTUAL_ENV when set
export VIRTUAL_ENV="$(realpath "$env_path")"
fi
prepare_env() {
echo "==> Syncing environment with uv..."
if [[ -n "$python_version" ]]; then
echo " Using Python $python_version"
uv sync --python "$python_version"
else
uv sync
fi
echo "==> Interpreter in use:"
uv run python -c 'import sys,platform; print(sys.executable); print(platform.python_version())'
}
# Run tasks
if $run_tests || $run_collectstatic; then
prepare_env
fi
if $run_tests; then
echo "==> Running tests..."
# If your DB user needs CREATEDB for Django's test DB, grant it separately.
if ! uv run python manage.py test; then
echo "Tests failed! Aborting."
exit 1
fi
fi
if $run_collectstatic; then
echo "==> Running collectstatic..."
if ! uv run python manage.py collectstatic --noinput; then
echo "collectstatic failed! Aborting."
exit 1
fi
fi
echo "==> Interpreter in use:"
uv run python -c 'import sys,platform; print(sys.executable); print(platform.python_version())'
echo "==> Reloading services..."
# Reload systemd and restart gunicorn units
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart gunicorn.socket gunicorn.service
systemctl reload nginx
echo "Done."
First, set strict mode:
set -Eeuo pipefail – “strict mode”:
-
-E– error traps propagate into functions. -
-e– exit if any command fails. -
-u– treat unset variables as errors. -
pipefail– A pipeline fails if any part fails, not just the last command.
Second, added the usage function, so help can be called: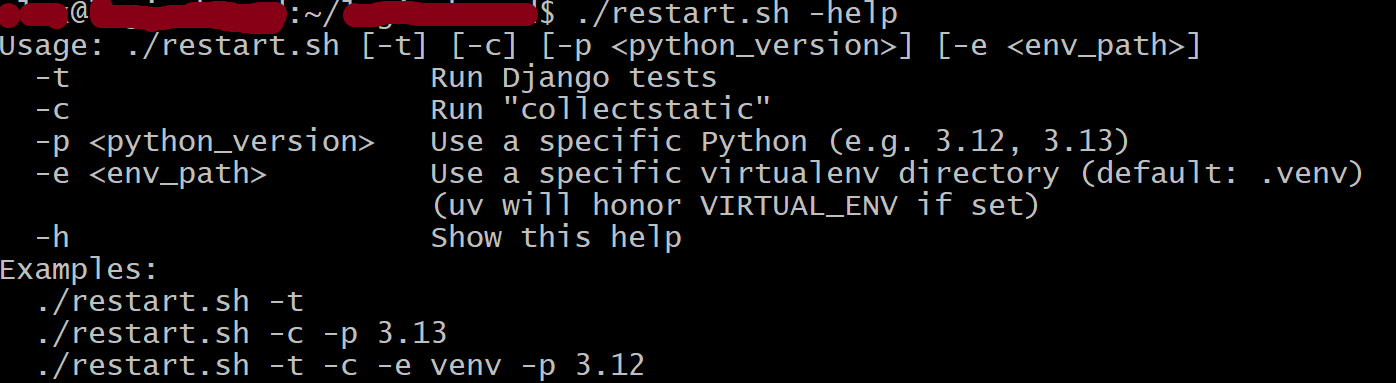
Third, I encountered a problem: when running the CI/CD pipeline, the root user did not see UV path, so I've added it in the script:
export PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$HOME/.cargo/bin:$PATH"
# This line adds two directories at the front of PATH:
# $HOME/.local/bin – where tools like uv are often installed for your user.
# $HOME/.cargo/bin – where Rust-installed tools live (also a common place for uv).
# :$PATH at the end keeps the original PATH too.
# export makes this new PATH visible to any commands the script runs.
UV_BIN="${UV_BIN:-$(command -v uv || true)}"
# This line sets a variable UV_BIN that should contain the full path to the uv executable.
# command -v uv
# Asks the shell: “Where is the uv command?”
# If found, it prints something like /home/user/.local/bin/uv.
# || true
# If command -v uv fails (no uv installed), the script won’t crash even if set -e is on. It # just returns an empty string instead of killing the script.
# "${UV_BIN:- ... }"
# If UV_BIN is already set (e.g. you ran UV_BIN=/usr/local/bin/uv ./restart.sh),
# then keep that value.
# Otherwise, use the result of command -v uv.
# So:
# “If the caller already told me where uv is, use that. Otherwise, try to find uv in PATH and store # its path in UV_BIN.”
if [[ -z "$UV_BIN" ]]; then
# [[ -z "$UV_BIN" ]] – checks if UV_BIN is empty (zero-length string).
# It will be empty if:
# uv wasn’t found in PATH and you didn’t set UV_BIN manually.
echo "uv not found on PATH: $PATH" >&2
# If it is empty:
# Print an error message.
# >&2 sends it to stderr (error output), not normal stdout.
exit 127
# Stop the script with exit code 127.
# 127 is the conventional “command not found” error code in shells.
# So:
# “If I still don’t know where uv is, fail early with a clear error and don’t continue.”
fi